"Christmas gift suggestions: To your enemy, forgiveness. To an opponent, tolerance. To a friend, your heart. To a customer, service. To all, charity. To every child, a good example. To yourself, respect." — Oren Arnold
A blog dedicated to process control, industrial instrumentation and measurement & control. Weekly posts highlighting educational, informative, and new product information on all aspects of process control equipment. Courtesy of Hile Controls, Inc. | Call us at 205.620.4000
Vortex Shedding Flowmeter Operating Principle
Measuring Principle - Kármán vortex street
This variety of flowmeter operates on the principle of Kármán vortex street, whereas any medium passing through the pipeline and flows around the bluff body, sheds a series of alternating vortices on each side of the body. This phenomenon is referred to as Vortex Shedding. These vortices shed downstream of the bluff body and dissipate as they flow further. This pattern of vortices is called a Kármán vortex street (also called a Von Kármán vortex street).Operation pf Vortex Flowmeter
A Vortex flowmeter primarily consists of a bluff body, a sensor assembly, and a transmitter. A bluff body or a shedder is nothing but a non-streamlined object or a barrier placed perpendicular to the axis of the pipeline, around which the medium flows.Calculation of the Mass Flow Rate
The frequency of the vortices, i.e. the number of vortices shed per second, is directly proportionate to the velocity of the medium. This Vortex Shedding Frequency is used to calculate the mass flow.The sensor assembly records the pressure and velocity oscillations generated on each side of the bluff body by the vortices and generate a digital linear output signal. The Vortex Shedding Frequency is calculated using the following formula:
f = St * V/d
Where:f = Frequency of Vortex Shedding St = Strouhal Number
V = Flow Velocity
d = Width of the Bluff Body
Strouhal Number St
The Strouhal Number in the above formula is also called as “reduced frequency”. It is a dimensionless param- eter that is a measure of the Vortex Shedding Frequency and the velocity of the flow medium. It is calculated using the formula:St = fd/U
Where:f = Frequency of Vortex Shedding d = Width of the Bluff Body
U = Velocity of the Flow Medium
The Strouhal Number is a function of the Reynold’s Number. Reynold’s Number is also a dimensionless parameter that is used to determine how the flow pattern of different fluids will change. The Strouhal Number should remain constant when the Reynold’s Number ranges from 2 × 104 to 7 × 106.
Calculation of Volume Flow Rate
When the Vortex Shedding Frequency is known, the volumetric flow rate can be calculated using the formula:q = f/k * d
Where:q = Volumetric Flow Rate
f = Vortex Shedding Frequency
k = k Factor, which is a ratio of the pulses transmitted to the unit volume.
You can download the TEK-TROL Tek-Vor 1300C Vortex Flowmeter Brochure from the Hile Controls of Alabama web site here.
For more information about vortex shedding flowmeters, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. Call them at 205-620-4000 or visit their web site at https://hilealabama.com.
The Advantages of Infrared Pyrometers, How Infrared Pyrometers Work, Where & Why Wavelength Matters, and Pyrometer Technologies
Temperature is commonly measured in manufacturing operations to monitor and control product quality and process productivity. Many applications use contact devices like thermocouples and RTDs, but all too often these devices are inaccurate, too slow, difficult to use, or require frequent replacement creating process downtime and reducing productivity. For many applications, infrared pyrometers are the perfect solution because they can accurately and reliably measure a target’s temperature without contact.
This brochure provides an excellent basic understanding of how infrared pyrometry works, different techniques for measuring temperature, and several types of industrial pyrometer.
For more information on industrial infrared pyrometers, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. Call them at 800-536-0269 or visit their web site at https://hilealabama.com.
This brochure provides an excellent basic understanding of how infrared pyrometry works, different techniques for measuring temperature, and several types of industrial pyrometer.
For more information on industrial infrared pyrometers, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. Call them at 800-536-0269 or visit their web site at https://hilealabama.com.
Thank You Veterans, for Serving Our Country and Protecting Our Freedom
Through the observance of Veterans Day, we remind ourselves of the bravery, sacrifice, and selflessness of the Veterans who serve our country and protect our freedom. By celebrating our Veterans, we continue to tell the story of how this country became the most powerful on Earth - through bravery, honor, truth, and determination.
To all military personnel who took an oath to defend the United States and our Constitution, from all enemies, foreign and domestic, we at Hile Controls of Alabama thank you.
Common Configurations for the ABB LWT300 Series Guided Waver Radar Transmitter
 |
| Storage tanks, liquid or solid. |
 |
| Agitated tank with stilling well. |
The ABB LWT300 Guided Wave Radar transmitters are equipped with on-board diagnostics that can be used for safety monitoring, improved reliability, downtime reduction, and performance verification.
The LWT300 series addresses several industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, chemical, power generation, water and wastewater, pulp and paper, and marine. To meet these challenging applications, this series of instruments offers a wide range of configurations.
USE ABB MODEL LWT310 FOR LIQUIDS
 |
| Horizontal tanks. |
USE ABB MODEL LWT320 FOR SOLIDS
The LWT320 fits in a 38 mm (1 ½ in) NPT interface and is offered in a flanged version.For solids applications, the LWT320 is recommended since it can withstand a higher pull force. The LWT320 is also useful for applications having a 38 mm (1 ½ in) NPT interface.
 |
| Agitated Tanks |
ABB LWT300 SPECIFICATION
- Temperature range: up to 200 °C (392 °F)
- Maximum process pressure: 200 bar (2900 psi)
- LevelExpert software for easy configuration, reliable surface detection and easy troubleshooting
- 2-wire powered and HART 7 communication
- SIL2
- Certified for potentially explosive atmospheres
ABB LWT300 APPROVALS
- CE
- FM/ATEX/IECEx hazardous area, flameproof, intrinsically safe methods of protection
- SIL 2 (no redundancy), SIL 3 (redundant configuration)
- CRN
 |
| Tanks with external chambers. |
Contact Hile Controls of Alabama with your ABB Level Instrumentation needs. They can be reached by calling 800-536-0269 or by visiting https://hilealabama.com.
The Jordan Mark 75 Control Valve
 The Jordan Valve Mark 75 wafer-style control valve provides you strong advantages in pricing, weight, capacity, and ease of maintenance. The wafer body means lower weight and size, which lowers cost. The Mark 75's lighter weight means you spend less time on installation and support.
The Jordan Valve Mark 75 wafer-style control valve provides you strong advantages in pricing, weight, capacity, and ease of maintenance. The wafer body means lower weight and size, which lowers cost. The Mark 75's lighter weight means you spend less time on installation and support.The wafer-style body and sliding gate combination gives you an operating Cv range from 8 to 600 for outstanding control. The Mark 75 also makes 180° rotation easier, as well as reversing of function and changing actuation because of its T-slot design.
JORDAN MARK 75 CONTROL VALVE HIGHLIGHTS
- Shorter stroke length than globe or cage designs
- Straight-through flow
- Ease of maintenance
- Easy installation between flanges with wafer body
- High flow rates
- Self cleaning, self lapping seats
- Reduced noise compared to conventional globe/ cage valves
- More resistant to cavitation / flashing with straight through, wafer design
Installed in a broad range of gas, chemical and steam applications all over the world, Jordan control valves have been providing unparalleled benefits to industrial manufacturers for over fifty years.
For more information about Jordan Valves, contact Hile Controls of Alabama by calling 800-536-0269 or by visiting https://hilealabama.com.
Labels:
Alabama,
control valve,
Florida Panhandle,
Jordan Valve,
Mark 75,
Mississippi
Selection and Calibration of a Turbine Flow Meter Whitepaper
Turbine flow meters have been an effective flow measurement technology for many years. Advancements in other measuring technologies in recent years have provided many options when selecting a meter for a flow measurement application. This has the benefit of allowing the user to select the measuring technology that provides the optimum characteristics for the specific application. The downside of all these measurement options is the user must have a significant understanding of many technologies in order to make the best educated decision when selecting the meter.

The intent of this paper, courtesy of FTI Flow Technology, is to provide the reader with a basic understanding of the operational characteristics and calibration methods of turbine flow meters. The information provided is targeted at liquid meter applications. Turbine meters are also successfully used in gas applications. The operational characteristics of gas meters are basically the same as liquid meters, however the calibration methods and procedures are worthy of a paper specific to gas applications and will not be address at this time.
Hile Controls of Alabama
https://hilealabama.com
800.536.0269

The intent of this paper, courtesy of FTI Flow Technology, is to provide the reader with a basic understanding of the operational characteristics and calibration methods of turbine flow meters. The information provided is targeted at liquid meter applications. Turbine meters are also successfully used in gas applications. The operational characteristics of gas meters are basically the same as liquid meters, however the calibration methods and procedures are worthy of a paper specific to gas applications and will not be address at this time.
Hile Controls of Alabama
https://hilealabama.com
800.536.0269
The Honeywell Analytics Searchzone Sonik™
Searchzone Sonik™ is a hazardous area certified advanced ultrasonic gas leak detector for detecting pressurized gas leaks. It provides local visual status indication as well as 4-20 mA with HART® and Modbus® outputs as standard. It has a Bluetooth® interface for configuration and maintenance using the Searchzone Sonik™ App on a suitable Bluetooth enabled smartphone or other suitable Android
device (mobile device).

The Searchzone Sonik™ detector is ATEX and IECEx approved for
use in either Zone 1 (gas) or Zone 21 (dust) hazardous areas as well as being cULus approved for use in Class I Division 1 or Class II Division 1 locations. See Certification and Approvals section of this manual for a list of certificates.

The Searchzone Sonik™ detector is available in painted Stainless Steel. It has two cable entries for easy wiring with either M25 or 3/4” NPT cable entries, dependent on the version.
Hile Controls of Alabama
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
device (mobile device).

The Searchzone Sonik™ detector is ATEX and IECEx approved for
use in either Zone 1 (gas) or Zone 21 (dust) hazardous areas as well as being cULus approved for use in Class I Division 1 or Class II Division 1 locations. See Certification and Approvals section of this manual for a list of certificates.

The Searchzone Sonik™ detector is available in painted Stainless Steel. It has two cable entries for easy wiring with either M25 or 3/4” NPT cable entries, dependent on the version.
Hile Controls of Alabama
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
Applications and Industries Using the ABB LMT Magnetostrictive Level Transmitter
This video outlines the primary industries and applications where the ABB LMT Series of level transmitters are used.
The ABB LMT Series of level transmitters is a modular range of field mounted, advanced microprocessor-based electronic transmitters, utilizing multiple sensor technologies. Accurate and reliable measurement of liquid level and interface are provided in even the most difficult and hazardous industrial environments. The LMT100 is also available with optional temperature measurement.
For more information on the ABB LMT series, contact Hile Controls of Alabama by calling 800-536-0269 or visit https://hilealabama.com.
Labels:
ABB,
Alabama,
Florida Panhandle,
level transmitter,
LMT,
LMT100,
LMT200,
magnetostrictive,
Mississippi,
Western Tennessee
Understanding Cascade Control Loops
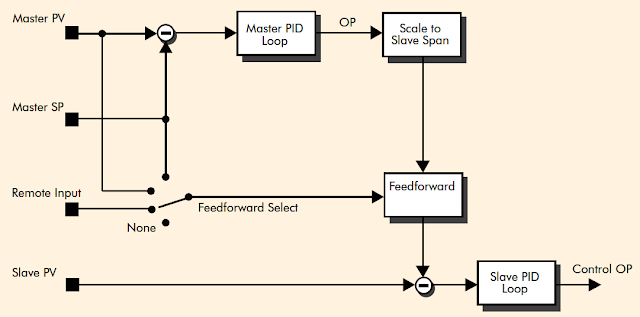 |
| Cascade with feedforward (image courtesy of Eurotherm). |
Cascade control is a technique used to enable processes with long lags to be controlled with the fastest possible response to process disturbances including setpoint changes, while still minimizing the potential for overshoot. This is achieved by controlling a secondary, more responsive process that influences the main process. The main process is controlled using a master PID loop, the output of which is used to determine the setpoint of the secondary process which is controlled by a second PID loop. This second loop is referred to as the slave loop.
Benefits of Cascade Control:
- Accurate control of load
- Compensation for process delays
- Overheating protection
- Optimum Process response
Cascade with feedforward
 |
| Vacuum heat treatment furnace. (Image courtesy of Eurotherm) |
Feedforward is an option available when using cascade control. It allows either the master PV, master SP or user defined variable to be fed forward so that it directly influences the slave setpoint (see diagram below).This minimizes the amount of work required from the master PID loop.
Master SP/PV feedforward
In this mode the feedforward limits are set directly in the slave loop’s engineering units, which also adjusts the gain of the feedforward path. In the case of PV feedforward this allows the difference between the master and slave PV’s to be limited and is often called “Delta T control”. This is used on reactor vessels and autoclaves to limit temperature gradients, thus minimizing processing time and ensuring consistent product quality.
Process feedforward
 |
| Pasteurization (image courtesy of Eurotherm). |
An example where cascade control with feedforward can be used is in pasteurization heat exchangers. The feedforward signal allows the controller to compensate for rapid variations in inlet flow therefore maintaining a stable outlet temperature.
Cascade Control is ideal for:
- Heat treatment furnaces
- Vacuum furnaces
- Autoclaves
- Semiconductor diffusion
- Batch reaction vessels
- Heat exchangers
- Crystal growth
- Distillation columns
Reprinted with permission from Eurotherm.
Guided Wave Radar vs. Differential Pressure Level Transmitter
An application guide courtesy of Tek-Trol Technology Solutions and Hile Controls of Alabama.
Differential Pressure (DP) transmitters can be traced back to the 1950s. Since then they have served as one the most popular technologies for fluid level measurement and have left their mark in process industry. The application range is vast and varies from chemical, petrochemical, and refineries to electric power generation and more. Over the years, Differential Pressure transmitters have single handedly dominated the worldwide market of process level measurement instruments with the largest sales volume.
Guided Wave Radar is a revolutionary method of liquid level measurement in which high-frequency electromagnetic waves are guided to travel from transmitter to the material to be measured. It works on the principle of Time Domain Reflectrometry (TDR).
This application guide provides a comparison between traditional Differential Pressure Level Transmitters and Guided Wave Radars for liquid level measurement applications by analyzing the features and benefits of both.
Hile Controls of Alabama
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
Differential Pressure (DP) transmitters can be traced back to the 1950s. Since then they have served as one the most popular technologies for fluid level measurement and have left their mark in process industry. The application range is vast and varies from chemical, petrochemical, and refineries to electric power generation and more. Over the years, Differential Pressure transmitters have single handedly dominated the worldwide market of process level measurement instruments with the largest sales volume.
Guided Wave Radar is a revolutionary method of liquid level measurement in which high-frequency electromagnetic waves are guided to travel from transmitter to the material to be measured. It works on the principle of Time Domain Reflectrometry (TDR).
This application guide provides a comparison between traditional Differential Pressure Level Transmitters and Guided Wave Radars for liquid level measurement applications by analyzing the features and benefits of both.
Hile Controls of Alabama
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
US Power Grids, Oil and Gas Industries, and Risk of Hacking
A report released in June, from the security firm Dragos, describes a worrisome development by a hacker group named, “Xenotime” and at least two dangerous oil and gas intrusions and ongoing reconnaissance on United States power grids.
Multiple ICS (Industrial Control Sectors) sectors now face the XENOTIME threat; this means individual verticals – such as oil and gas, manufacturing, or electric – cannot ignore threats to other ICS entities because they are not specifically targeted.
The Dragos researchers have termed this threat proliferation as the world’s most dangerous cyberthreat since an event in 2017 where Xenotime had caused a serious operational outage at a crucial site in the Middle East.
The fact that concerns cybersecurity experts the most is that this hacking attack was a malware that chose to target the facility safety processes (SIS – safety instrumentation system).
For example, when temperatures in a reactor increase to an unsafe level, an SIS will automatically start a cooling process or immediately close a valve to prevent a safety accident. The SIS safety stems are both hardware and software that combine to protect facilities from life threatening accidents.
At this point, no one is sure who is behind Xenotime. Russia has been connected to one of the critical infrastructure attacks in the Ukraine. That attack was viewed to be the first hacker related power grid outage.
This is a “Cause for Concern” post that was published by Dragos on June 14, 2019.
“While none of the electric utility targeting events has resulted in a known, successful intrusion into victim organizations to date, the persistent attempts, and expansion in scope is cause for definite concern. XENOTIME has successfully compromised several oil and gas environments which demonstrates its ability to do so in other verticals. Specifically, XENOTIME remains one of only four threats (along with ELECTRUM, Sandworm, and the entities responsible for Stuxnet) to execute a deliberate disruptive or destructive attack.
XENOTIME is the only known entity to specifically target safety instrumented systems (SIS) for disruptive or destructive purposes. Electric utility environments are significantly different from oil and gas operations in several aspects, but electric operations still have safety and protection equipment that could be targeted with similar tradecraft. XENOTIME expressing consistent, direct interest in electric utility operations is a cause for deep concern given this adversary’s willingness to compromise process safety – and thus integrity – to fulfill its mission.
XENOTIME’s expansion to another industry vertical is emblematic of an increasingly hostile industrial threat landscape. Most observed XENOTIME activity focuses on initial information gathering and access operations necessary for follow-on ICS intrusion operations. As seen in long-running state-sponsored intrusions into US, UK, and other electric infrastructure, entities are increasingly interested in the fundamentals of ICS operations and displaying all the hallmarks associated with information and access acquisition necessary to conduct future attacks. While Dragos sees no evidence at this time indicating that XENOTIME (or any other activity group, such as ELECTRUM or ALLANITE) is capable of executing a prolonged disruptive or destructive event on electric utility operations, observed activity strongly signals adversary interest in meeting the prerequisites for doing so.”
The Jordan Mark 75 Sliding Gate Control Valve: Better Control, Lower Total Installed and Operating Cost
Looking for outstanding control and high flow in a small package? Say hello to the Jordan Valve Mark 75 Sliding Gate Control Valve! The wafer style body and the unique Sliding Gate seat design combine to provide accurate control in a very small package.
Mark 75 Features / Benefits
Sliding Gate Seat
- Shorter Stroke = smaller actuators – Save on air
- Easy maintenance
- Quiet operation
- High turndown
Available in a Variety of Materials
- Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Monel, Duplex, Hastelloy, and more
- Stainless Steel Yoke
- Namur compliant yoke allows mounting of positioners and other accessories
For more information, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. Call 800-536-0269 or visit https://hilealabama.com.
Understanding Guided Wave Radar Transmitters
 |
| Guided wave radar Transmitter (ABB) |
Guided wave radar transmitters are widely used across different industries. These devices with their simple installation and trouble-free operations help industrial companies save time and money. They are ideal for a large number of process applications ranging from simple to complex.
How Do Guided Wave Radar Transmitters Work?
Guided wave radar transmitters rely on microwave pulses. Since microwaves are not affected by dust, pressure, temperature variations, and viscosity, this type of transmitter produces highly accurate results.
A low-energy microwave pulse is sent down a probe, and a part of it is reflected back when the pulse hits the process media. The liquid level is directly proportional to the time-domain reflectometry. The time when the pulse is launched and received back is measured to determine the distance from the surface of the media.
Types of Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitters
 Guided wave radar level transmitters are available in different probe configurations. Selecting the right probe is important for successful implementation of the device. While manufacturers offer a range of guided wave radars, most are derived from the three basic probe configurations: single element, twin element, and coaxial.
Guided wave radar level transmitters are available in different probe configurations. Selecting the right probe is important for successful implementation of the device. While manufacturers offer a range of guided wave radars, most are derived from the three basic probe configurations: single element, twin element, and coaxial.
Single element probe — The single element probe is the most widely used and least efficient device. The device is popular since it is more resistant to the coating of the liquid.
Twin element probe — The twin element probe is a good, general purpose probe that is generally used in long-range applications. They are ideal in situations where flexible probes are important for successful reading.
Coaxial probe — The coaxial probe configuration is the most efficient guided wave radar level transmitters. The probes are used in more challenging low-dielectric applications.
Benefits of Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitters
Guided wave radar level transmitters provide a range of benefits in different applications. The concentration of the measuring signal is strong and clean. This is due to the narrow path of the signal propagation that reduces the chances of impact by stray signals due to obstacles or construction elements inside the tank.
Another benefit of guided wave radar level transmitters is that they are easy to install. No mounting holes are required to install the device. This results in cost savings for the organization. The waveguide can be formed to follow the tank’s contours or mounted at an angle.
The device is ideal in situations where an interface measurement is required. The measuring signals can penetrate the medium deeply, resulting in more accurate results. The waveguide technology is suitable for applications where the medium is subjected to heavy vapors, foam, and dust.
Guided Wave instruments can detect changes in dielectric consents on the boundary of a property. The device can be configured to detect level at both the top and the bottom of a layer of emulsion.
Industrial Application of Guided Wave Radar
Guided wave radar level transmitters are increasingly being used in process industries. The sensors are used in situations that previously employed ultrasonic, hydrostatics, and capacitance. The accuracy specification of the basic model range is up to ±5mm, while the accuracy of the advanced models is up to ±2mm.
The device is generally used in industries to take level readings. The readings are used for local indication and visualization in control systems.
Moreover, guided wave radar level transmitters are also used for managing liquid inventory, determining safety limits, dry run protection, and leak detection. Other applications of guided wave radar level transmitters include communicating low limits to suppliers, automated ordering systems, and streamlining the logistics process.
Guided radar level measurement is also suitable for bulk solids. The surface type is not restricted to liquids since the reflected waves are guided easily through any medium. Foam formation and turbulent liquid surfaces and different angled surfaces (as is the case with bulk solids) don’t influence the accuracy of the reading.
Selection of Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitters
Selection of guided wave radar level transmitters should be based on the requirements of the task. Generally, the rigid single element probe configuration is ideal for angled installations for flowing liquids. The dual flexible wire probe is suitable for most other common applications.
A coaxial probe configuration is recommended for liquids that are cleaner with low dielectric constant and with turbulence on the product’s surface. This type of guided wave radar device is also recommended for installations where the probe is near the tank wall or other obstacles.
Make sure that the device can withstand the range of temperature within the tank. Most GWR devices are rated up to 850 deg F or 450 deg C. You should select a device with added signal strength since this will result in increased reliability and accuracy of the devices.
Guided wave radar level transmitter with dynamic vapor compensation is recommended where a high level of accuracy is required under a high-pressure environment. The measurement taken from the device can compensate for changes in vapor dielectric, which results in improved accuracy.
Other factors that should be considered include mounting and proximity. Single probe configuration can be installed almost anywhere. But the single probe configuration can only to apply to specific situations.
Lastly, the probe length of the device should be of the right length. The length should be according to the measurement rate. This is an important consideration as it can help in ensuring accurate reading with minimum chances of an error.
Guided Wave radar level transmitters can also be used with an agitator. However, certain things must be considered prior to use the device. The probe must be prevented from contacting the agitator blades. Make sure that you confirm the ability of the probe to withstand the force inside the medium. This is important since turbulent on the surface may decrease the accuracy of the measurement. You can install the device in a bypass chamber or stilling well for an agitated tank.
The consultation with an applications expert is strongly suggested before any specification or application is configured. Doing so will assure a safe and efficient operation.
For more information about guided wave radar level transmitters, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. Call 800-536-0269 or visit https://hilealabama.com.
Coriolis Flowmeters
 |
| U Shaped Coriolis flowmeters in field. (Tektrol) |
Coriolis flowmeters are used in a variety of industries ranging from oil and gas, petrochemicals, and food to chemical, life sciences, and — particularly — in transfer applications.
How Does a Coriolis Flow Meter Work?
Coriolis flowmeters work on the principle of Coriolis Force that was first explained by a French engineer and mathematician Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis in the 19th century. The Coriolis force represents an inertial force that acts on bodies in a rotating frame of reference.
 |
| Diagram of Coriolis flow measuring sensor. |
Coriolis meters have sensors inside the measuring flow tube made of magnet and coil assemblies. The sensors are located both at the inlet and outlet of the tube. A voltage in the form a sine wave is created as the coils move through the magnetic field.
The sine waves are in phase with each other when there is no liquid flow. Once the liquid flows through the tube, the measuring tubes twist depending on the mass flow. The sensors detect the extent of the twist by assessing the phase shift in the sine waves. The difference in phase shift helps in determining the mass flow rate.
Volumetric flow is determined by dividing the mass flow rate by the density of the liquid.
Density change is determined by assessing the change in oscillation frequency in response to the excitation inside the tube. The higher the mass flow rate, the lower will be the frequency change and density of the liquid flow.
 Lastly, Coriolis flowmeters can also be used to measure the temperature inside the tube. The device has sensors inside the tube that can detect temperatures of up to 752 F or 400 C.
Lastly, Coriolis flowmeters can also be used to measure the temperature inside the tube. The device has sensors inside the tube that can detect temperatures of up to 752 F or 400 C.The Pros and Cons of Coriolis Flow Meters
Coriolis flow meters can assess liquid flow in both forward and reverse directions. Advanced Coriolis meters have dual curved tubes that can measure with more accuracy. Moreover, the device with curved tubes is characterized by lower pressure drop, making them ideal in specific situations such as wastewater handling, chemical processing, pulp and paper processing, and oil and gas industries.
Another application of Coriolis flow meters is in the pharmaceuticals and food and beverage industries. They can be used with a straight tube design so they are easy to clean. The flowmeters are also used in scientific studies for measuring corrosion and assessing liquids and gases. In addition, the flowmeters are used in mining operations to monitor liquid flow rate.
While Coriolis meters allow accurate assessment of fluid flow, they are not free from errors. The
device can show inaccurate reading when air bubbles are present. The bubbles create splashing that results in generate inaccurate readings. They change the energy required for tube oscillation, resulting in a false assessment of fluid flow.
A lot of energy is spent in the vibration of the tube, especially in case of large spaces. This can also result in failure of accurate assessment of liquid flow inside the tube.
Installation and Calibration of Coriolis Flow Meter
Coriolis flowmeter must be installed with full liquid so that no air gets trapped inside the tube. The meter should also be drained completely before use. The ideal location for the flowmeter is a vertical pipe mount with an upward flow of fluid.
The Reynolds number is not a limitation with the Coriolis meter. In addition, there is no need for accounting for swirl and velocity profile distortion. As a result, the device can be used without adjusting for straight runs of relaxation piping to condition the liquid flow.
An air release upstream of the meter should be installed if there is a likelihood of air bubbles. In addition, filters, strainers, or air/vapor eliminators can help prevent air bubbles inside the tube. Control valves can also be installed to increase the back-pressure and reduce the likelihood of flashing.
For more information on Coriolis flowmeters contact Hile Controls of Alabama by calling 800-536-0269 or by visiting https://hilealabama.com.
ABB LWT300 Series Guided Wave Radar Data Sheet
 With fast and reliable settings, ABB's LWT300 series of instruments emphasizes measurement made easy. With its LevelExpert technology based on 20 years of experience, simply enter installation data and basic process conditions, and let LevelExpert do the rest: no echo mapping or baseline correction required.
With fast and reliable settings, ABB's LWT300 series of instruments emphasizes measurement made easy. With its LevelExpert technology based on 20 years of experience, simply enter installation data and basic process conditions, and let LevelExpert do the rest: no echo mapping or baseline correction required.Unlike traditional guided-wave radars that use device parameters requiring multiple adjustments, the LWT300 series of instruments does it for you. The instrument uses built-in intelligence to differentiate between the actual level and other false signals. It also keeps monitoring all these false signals while maintaining a reliable level reading. It is like having a level expert in each device.
Hile Controls of Alabama
The ABB LWT Series Guided Wave Level Transmitter with LevelExpert
This video introduces the LWT Series level transmitters from ABB.
The ABB LWT Series is a family of guided wave radar transmitters utilizing the most advanced level algorithm, LevelExpert. With LevelExpert, you no longer need to be an instrument expert to accurately control level. With the LWT Series, the expert is inside.
Main Features:
To meet the most challenging level applications, the LWT300 series of instruments offers a wide range of configurations.
Temperature range: -45 to 200 °C (–49 to 392 °F) Maximum process pressure: vacuum to 200 bars (2900 psi)
• LevelExpert software for easy configuration, reliable surface detection and easy troubleshooting
• 2-wire powered and HART 7 communication
• SIL2 (no redundancy), SIL 3 (redundant configuration)
• Certified for potentially explosive atmospheres
For more information, contact Hile Controls of Alabama:
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
The ABB KM26 Magnetic Level Gauge: Design, Features, Applications
The ABB KM26 Magnetic Level Gauge provides custom engineered solutions to liquid level applications in industries such as: oil and gas, refinery, chemical, petrochemical, power generation and many more.
The KM26 MLG has proven itself to be a safe, reliable, maintenance free solution for total and/or interface level detection in toxic, corrosive, high pressure and high temperature processes.
Hile Controls of Alabama
800-536-0269
White Paper: The Benefits of Two-Leg Three Phase Power Control
 White paper courtesy of Eurotherm Schneider Electric.
White paper courtesy of Eurotherm Schneider Electric.Traditionally, three-leg power control is used in three phase heating applications. However, in some cases three-leg control is not a necessity and two-leg control can be a better option. Technological developments in SCR (silicon controlled rectifier) power controllers have resulted in new products and methods that can reduce both CAPEX and OPEX in these situations.
This paper discusses the benefits of utilizing two-leg power control in the EPower advanced SCR power controller, compared with traditional three-leg control.
You can download the entire Eurotherm white paper from this page on the Hile Controls of Alabama web site.
Identifying the Components and Construction of the Autrol APT3500 Smart Pressure Transmitter
The Autrol APT 3500 Smart Pressure Transmitter is a microprocessor-based high-performance transmitter, which has flexible pressure calibration and output, automatic compensation of ambient temperature and process variable, a configuration of various parameters, communication with HART protocol. The application is very various, as measuring liquid, gas or steam flow as well as pressure and liquid level by an application method. All data of the sensor is to be input, modified and stored in EEPROM.
For more information about Autrol instrumentation, contact Hile Controls of Alabama.
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
Innovative DEVCOM 2000 Converts Ordinary Laptop PC's into Full-featured HART Communicator
ProComSol is the creator of the innovative DEVCOM 2000 SMART device communicator, a breakthrough that converts an ordinary laptop PC into a full-featured HART communicator. With the DEVCOM 2000 software and a HART modem you can configure transmitters and control valves on the bench or in the field quickly, easily and economically.
For unprecedented levels of convenience, efficiency, and safety, the DEVCOM 2000 system is also available with Bluetooth capability for communication with field devices. This can be handy for devices installed in unsafe or difficult to reach locations. ProComSol, which stands for "PROcess COMmunication SOLutions", is the leading provider of field-proven HART communication solutions for industrial applications, and was the first to deploy Bluetooth technology to configure and troubleshoot transmitters and control valves.
 ProComSol developed the DEVCOM 2000 software on the PC platform because it offers the
ProComSol developed the DEVCOM 2000 software on the PC platform because it offers the
advantages of a powerful and flexible, yet familiar and intuitive, tool to meet many of your industrial automation needs. For example, the PC can effectively store and present configuration tools user manuals, operating procedures, reports, and a host of other tools. Configurations can be saved as PDF files in order to keep a record of all up-to-date configurations of your devices. The PC makes it easy to integrate HART information into your reports and emails. This not only gives you the potential for system-wide productivity increases, but also eliminates the need to purchase and maintain a separate handheld HART communicator.
The DEVCOM 2000 software has been tested and proven by more than a thousand users in many industries including oil and gas refining, chemical and petrochemical, power generation, water and wastewater, pharmaceuticals, pulp and paper, mining and metals, and food and beverage. Quality is an integral part of the design, development, and production of ProComSol products. Their quality management system has been certified to ISO 9001.
Last, but not least, unlike handheld HART communicators that typically cost between $4000 and $7000 dollars, the DEVCOM 2000 system costs approximately $1000 and can be easily and economically upgraded to include additional functions as they become available. Each DEVCOM 2000 comes complete with warranty and free software upgrades during the first year of ownership.
The DEVCOM 2000 Windows Explorer interface is intuitive and easy to use. Menus's are clearly available, as are the variables list. Because it's on the computer screen, the menu structure can be expanded or contracted as required so there is no need to dig through small device menus to perform a task. With the full keyboard available, data entry is also easy. The computer screen continuously displays the variables, with items in bold being editable and items in grey being read-only. Edited variables are shaded in yellow, which means the variable has been edited but not yet committed to the device. After clicking on the send icon, the yellow shading goes away and the variable has been changed in the device. It's that simple.
HART Protocol's popularity is partially based on the ability to "get data out of the field device" through a data file called a Device Description (DD). The DEVCOM 2000 includes a list of DD's in the DEVCOM 2000 software. The DEVCOM 2000 uses the compiled device description binary file the DD developed by the device manufacturer and registered with the HART Communication Foundation. Each DD has been tested by the device manufacturer. This is an important point because we know that every DD will work with the device be it a transmitter or control valve. The Windows Explorer interface enables other DD's to be easily added in the field. In fact, because it's so easy to add DD's in the field, many device manufacturers are using DEVCOM 2000 to test new DDS that they are currently developing. The DD library is updated and published four times per year by the HART Communication Foundation and new DEVCOM 2000 updates are available shortly after. Updates can be downloaded for free from the ProComSol website during the one-year warranty period, and in subsequent years by paying a nominal library subscription fee.
For more about DEVCOM 2000 or any ProComSol product, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. They can be reached by phone at 800-536-0269 or by visiting https://hilealabama.com.
For unprecedented levels of convenience, efficiency, and safety, the DEVCOM 2000 system is also available with Bluetooth capability for communication with field devices. This can be handy for devices installed in unsafe or difficult to reach locations. ProComSol, which stands for "PROcess COMmunication SOLutions", is the leading provider of field-proven HART communication solutions for industrial applications, and was the first to deploy Bluetooth technology to configure and troubleshoot transmitters and control valves.
 ProComSol developed the DEVCOM 2000 software on the PC platform because it offers the
ProComSol developed the DEVCOM 2000 software on the PC platform because it offers the advantages of a powerful and flexible, yet familiar and intuitive, tool to meet many of your industrial automation needs. For example, the PC can effectively store and present configuration tools user manuals, operating procedures, reports, and a host of other tools. Configurations can be saved as PDF files in order to keep a record of all up-to-date configurations of your devices. The PC makes it easy to integrate HART information into your reports and emails. This not only gives you the potential for system-wide productivity increases, but also eliminates the need to purchase and maintain a separate handheld HART communicator.
The DEVCOM 2000 software has been tested and proven by more than a thousand users in many industries including oil and gas refining, chemical and petrochemical, power generation, water and wastewater, pharmaceuticals, pulp and paper, mining and metals, and food and beverage. Quality is an integral part of the design, development, and production of ProComSol products. Their quality management system has been certified to ISO 9001.
Last, but not least, unlike handheld HART communicators that typically cost between $4000 and $7000 dollars, the DEVCOM 2000 system costs approximately $1000 and can be easily and economically upgraded to include additional functions as they become available. Each DEVCOM 2000 comes complete with warranty and free software upgrades during the first year of ownership.
The DEVCOM 2000 Windows Explorer interface is intuitive and easy to use. Menus's are clearly available, as are the variables list. Because it's on the computer screen, the menu structure can be expanded or contracted as required so there is no need to dig through small device menus to perform a task. With the full keyboard available, data entry is also easy. The computer screen continuously displays the variables, with items in bold being editable and items in grey being read-only. Edited variables are shaded in yellow, which means the variable has been edited but not yet committed to the device. After clicking on the send icon, the yellow shading goes away and the variable has been changed in the device. It's that simple.
HART Protocol's popularity is partially based on the ability to "get data out of the field device" through a data file called a Device Description (DD). The DEVCOM 2000 includes a list of DD's in the DEVCOM 2000 software. The DEVCOM 2000 uses the compiled device description binary file the DD developed by the device manufacturer and registered with the HART Communication Foundation. Each DD has been tested by the device manufacturer. This is an important point because we know that every DD will work with the device be it a transmitter or control valve. The Windows Explorer interface enables other DD's to be easily added in the field. In fact, because it's so easy to add DD's in the field, many device manufacturers are using DEVCOM 2000 to test new DDS that they are currently developing. The DD library is updated and published four times per year by the HART Communication Foundation and new DEVCOM 2000 updates are available shortly after. Updates can be downloaded for free from the ProComSol website during the one-year warranty period, and in subsequent years by paying a nominal library subscription fee.
For more about DEVCOM 2000 or any ProComSol product, contact Hile Controls of Alabama. They can be reached by phone at 800-536-0269 or by visiting https://hilealabama.com.
Hazardous Gas Detection: Selecting the Right Device
 |
| Sensepoint Flammable and Toxic Gas Detector (Honeywell) |
Reprinted from an original article by Don Galman of Honeywell Analytics
There are many gas detection products on the market that might appear to be the same, but a closer inspection of specification, functionality and features reveals major differences in what products can do and the potential value they can offer. Similarly, individual applications are also unique in their respective designs, needs and processes undertaken.
KNOW YOUR SITE RISKS
Before beginning to consider gas detection equipment, a risk assessment needs to be conducted. Any company employing staff has the obligation to conduct risk assessments to identify potential hazards and these can include potential gas, vapor or Oxygen deficiency risks. If gas hazards are identified, gas detection is applicable as a risk reduction method.
IDENTIFYING THE PRIME OBJECTIVE
Depending on the processes being undertaken and the gases being detected, remote or off-site alarm notification plus event data logging/reporting may also be required for Health and Safety management records. Another factor impacting on the need for enhanced reporting functions might be regulatory compliance or a condition of insurance.
ASK THE RIGHT QUESTIONS
Having identified the primary objective, the suitable equipment is selected by asking a number of key questions. These fall into three broad categories:
- The gases to be detected and where they may come from
- The location and environmental conditions where detection is to take place
- The ease of use for operators and routine servicing personnel
 |
| Honeywell Analytics XNXUniversal Transmitter |
The gases to be detected should be identified by the risk assessment, however experienced gas detection equipment manufacturers and their approved distributors are often able to help in this process, based on their experience of similar applications. However, it is important to remember that it is the end-user’s responsibility to identify all potential hazards.
It is also essential to identify the potential source of a gas release as this helps determine the number and location of detectors required for a fixed gas detection system.
CONSIDER THE ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
The performance, accuracy and reliability of any gas detection equipment will be affected by the environmental conditions it is subjected to. Temperature, humidity and pressure levels at the location all have a direct bearing on the type of equipment that should be selected. Additional factors such as potential variations resulting from a production process itself, diurnal/nocturnal fluctuations and seasonal changes may also affect the type of device which is suitable.
UNDERSTAND PRODUCT FUNCTIONALITY
The next area of consideration relates to additional product functionality. Aspects like wiring configuration are important, especially when retro-fitting into an existing application. If the apparatus is being integrated into a separate safety system, certain communication protocols may also be required such as HART®, Lonworks or Modbus®.
Consideration will also need to be given regarding the requirement for local displays on transmitter units and local configuration of the unit and gas displays may also be a useful addition.
MEASURE THE EASE OF USE FOR OPERATORS AND ROUTINE SERVICING PERSONNEL
Routine maintenance is another important consideration. Some gases and vapors can be detected with a number of different sensing technologies, e.g. Hydrocarbon gases with catalytic beads or Non-dispersive Infrared NDIR. Catalytic beads do not provide fail-to-safety operation and therefore can require a high frequency of routine maintenance, however NDIR based solutions tend to have a higher initial purchase price, but may require less routine maintenance. In-house resource to undertake such routine maintenance needs to be identified and in the absence of such a resource, budgeting for third party maintenance is an important factor in selecting the right equipment.
For more information about Honeywell Analytics gas detection solutions, contact Hile Controls of Alabama by visiting their web site (https://hilealabama.com) or calling 800-536-0269.
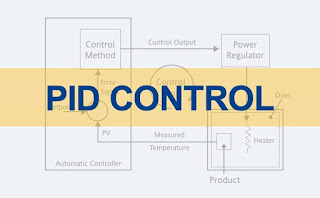
Principles of PID Control and Tuning White Paper
PID is short for "proportional plus integral and derivative control", the three actions used in managing a control loop. Process loop controllers use one, two or all three of these to optimally control the process system. PID control is used in a wide variety of applications in industrial control and process system management.
Download "Principles of PID Control and Tuning" from the Hile Controls website here.
Courtesy of Eurotherm. Eurotherm offers a wide range of single & multi-loop PID controllers.
Download "Principles of PID Control and Tuning" from the Hile Controls website here.
Courtesy of Eurotherm. Eurotherm offers a wide range of single & multi-loop PID controllers.
Tutorial on Setting Up the Jordan Valve Mark 70SP Series Sliding Gate Control Valve
The Jordan Mark 70SP Series is a line of pneumatically operated diaphragm control valves that combine multiple spring actuators with the precision of Jordan Valve's advanced sliding gate seat for closer control and greater accuracy.
Consisting of a modulating disc and stationary plate, the sliding gate seat components are slotted with multiple orifices that align to provide the precise flow needed to maintain the process requirements. The valve strokes in a fraction of the travel required by conventional control valves for rapid correction of any deviation from the process setpoint.
Jordan's unique sliding gate control valve trim teams up with pressure, temperature pH, level, or flow controllers for fast response, long term reliability, and high levels of accuracy on steam, gas, liquid and chemical services.
For more information about all Jordan Valve products, contact Hile Controls of Alabama by calling 800-536-0269 or visiting https://hilealabama.com.
The ABB LMS200 Magnetic Level Gauge Switch
 If you're looking for reliable liquid level detection from a non–invasive, non–contact, and economical device, ABB has a solution you need to consider.
If you're looking for reliable liquid level detection from a non–invasive, non–contact, and economical device, ABB has a solution you need to consider.
ABB’s magnetic level gauge switches provide safe and reliable liquid level detection and process control when integrated externally on the KM26 series magnetic level gauges and LS series products. The LMS200 series are non–invasive magnetically actuated electrical switches that provide complete isolation from the process fluid by coupling with the magnetic floats and attraction sleeves already present in the ABB KM26 and LS series magnetic level gauge.
This passive, method of coupling facilitates safe operation, while also eliminating the need for costly seals, diaphragms, and process connections commonly associated with point level switch technology. The superior design enables the setpoint to be adjusted without any changes to process piping, resulting in level switches that are quickly deployed, readily adjustable, and easy to maintain.
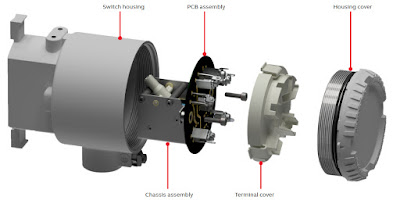 |
| LMS200 Magnetic Level Gauge Switch (exploded view) |
 |
| Wiring |
 |
| Mounting |
For more information on the LMS200 Magnetic Level Gauge Switch, or any ABB process level product, contact Hile Controls of Alabama.
https://hilealabama.com
800-536-0269
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)